- The Concern
- Applications
- Education ERP System
- Hotel Management System
- XeniaS Restaurant Software
- Content Management System
- Online Newsletter
- Attendance Management System
- Payroll System
- Doctors Schedule & Appointments Management System
- Online Shopping Cart
- Alumni Management System
- Stock Management System
- Online Admission System
- Online Examination System
- Online Learning System
- Tourism Automation System
- Library Management System
- Products & Services
- Sectors
- Support
- Reach Us
- Billing
- Blog
- Artificial Intelligence Positive Impact in Todays Life
- Why Cyber Security is important in today's life
- Artificial Intelligence Negative Impact in Todays Life
- Google knows you better than you know yourself
- Impact of YouTube in Today's World
- Digital Trust in Technology
- How Robotic Process Automation is impacting today's life
- What's Trending in Web Development 2023?
- Why digital trust is important for the digital services?
- Negative Impact of YouTube In today's World
- What is edge-computing?
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- About the buzzword named DevOps
- Cloud Computing
- Augmented Reality
- Future of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 5G status in India
- How Technology is changing the HealthCare Industry
- Need of Automation in Today’s World
- Brain computer assistance
- Smart Devices in Today’s Life
- Role of Biometrics
- Blockchain
- Replaceable battery in Smartphones is coming back
- Difference between VFX, CGI and SFX
- After DTH, it is DTM (Direct to Mobile) TV on Phone without Internet coming soon
- 3D Printing (A New Innovation)
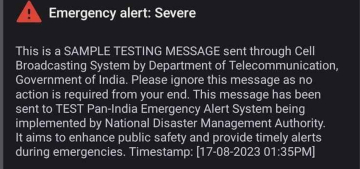
- Government’s initiative on emergency mobile alert system
- Constant Evolving Cyber Security
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
- Impact of smartphones on TV market
- Current Situation of IT Sector in India
- How Virtualization is changing Automation
- Natural Language Processing
- Apple considered switching to DuckDuckGo from Google for Safari
- How smartwatches have made our life easier
- Difference between Flagship phones and non-flagship phones
- Be safe from Dark Web
- Digital Transformation
- Use of drone to transportation in medical, commercial, utility sector
- Difference between Edge Computing and Fog Computing
- Additive Manufacturing
- Biometric - Attendance Management System
- Importance of IT sector in today’s world
- End of Work from Home [WFH] Era
- Top 5 Upcoming Technology
- Apple introduces new Apple Pencil with USB-C charging
- Smarter Devices
- Reliance Jio demonstrates its satellite- based gigabit internet in India
- Tata to make iPhones in India for local and global markets, Indian IT minister confirms
- Encryption and Decryption
- Futuristic Mobile Phones
- Bridging the Digital and Physical World
- How Google Maps solved India’s street name problem; Former employee explains
- Strategic Technology Trends – How they impact business goals.
- Why Google has paid a hefty sum to Apple to be in Search engine
- Meta launches AI based video editing tools
- OpenAI [known for ChatGPT] co-founder Sam Altman was fired last week, then almost rehired over the weekend
- Breakthrough Progress in Hologram Technology
- India’s government has issued a warning to social media giants Facebook and YouTube, to enforce rules against spread of deepfakes.
- The Action taken by Countries other than India against Deepfakes
- Governments’ initiative with Gajraj AI to save Elephant hit by trains
- Inactive Google accounts to be deleted from 1st of Dec 2023
- The VoLTE age is over, get ready for Vo5G
- YouTube launched Brand Connect and Podcast Features for creators in India
- Bluetooth scam
- Google Maps is changing in India
- Use of technology in cricket is getting advanced
- WhatsApp to end providing free google drive storage for photos videos and chat history
- Google Chrome tests blocking third party cookies
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
- AI advancements will drive even more energy usage
- Best “Wear OS” apps to install on your smartwatch in 2024
- Open AI trying to breach privacy – Reported by Garante
- Not Chasing DSLRs anymore, now smartphones are giving a huge competition in terms of good quality pictures and videos
- India shipments tops in smartphones selling
- An important news for all the Paytm users
- Another milestone for Indian payment system UPI
- Be Aware of Visa Scams
- Google Chrome Users should be aware of the new vulnerabilities
- Online Doctor Appointment Management System
- Sam Altman (Founder of OpenAI) is all set to comeback with his new initiative to the Tech industry
- OpenAI is introducing a new personal memory feature for ChatGPT
- Gemini AI image generator has been stopped temporarily by Google over inaccurate results
- India will play an important role in helping make sure AI is built responsibly
- Meta and LG announce collaboration to create advanced XR Technologies
- Collaboration between this companies to lead the digital transformation of the media and entertainment industry
- Tumblr and WordPress, both popular platforms, are reportedly selling user data to two AI giants
- AI models are well-crafted, leading to more accurate and relevant outputs than humans
- Meta sues former ‘disloyal’ executive, accused of stealing important documents
- Google had pledged $26.98 million to help people in Europe learn to use AI
- To cement its supremacy over the AI sector, Nvidia has unveiled its flagship AI chip
- By breaking language barriers, and ensuring equal users for all access through Universal Acceptance
- Microsoft asserts that customer data is not used for training models without permission and is not shared with third parties
- The lawsuit accuses Apple of abusing its power by restricting access to its hardware and software
- A class-action lawsuit settlement between google and users who claimed Google tracked their browsing activity even in “incognito mode”
- Small AI models like Phi-3 are gaining traction for their cost-effectiveness and suitability for personal devices, offering optimal performance without compromising on functionality
- New Scam Alert – “Hello? Hello?...” and the call is cut, and here all your bank balance vanish in one go
- Your number will be blocked within 2hours press 9... In the name of TRAI new scam has knocked the door
- Photos in Google Library are been unmanageable
- Disadvantages of Free SSL vs Advantages of Paid SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
- The Northern Lights effect on Technology
- The transformative power of AI in the hospitality industry
- Tech companies are firing their employees due to its technological advances
- USA aims to stay ahead with China in the realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- NFC card’s purpose, use, and examples
- The importance of Software Developers Company
- Low Coding Development
- SCAM ALERT!! All India Pregnant Jobs: A Tricky Plan To Be Aware Of -
- No Code Development
- Review of the Apple iPad Mini :
- To compete with the iPad, Google is probably converting Chrome OS to Android
- WARNING!! Avoid being fooled: Sextortion email scams are conducted by hackers using authentic Microsoft email addresses:
- Google Circle to Search will soon have a new app drawer and a redesigned user interface: This is how it seems.
- Know your google map better: Tips and Techniques
- Microsoft launches a $4 million bug bounty hacking competition at Ignite 2024:
- An AI-powered fashion expert is Google's Best App of 2024 in India
- At Ignite 2024 Microsoft will demonstrate AI agents capable of performing tasks on their own:
- Teachers can receive free AI training from Open AI :
- Meta intends to challenge the India antitrust ruling on WhatsApp because it disagrees with it.
- Global rules and standards for AI are desired by more than 81% of corporate executives according to the TCS Report
- Release of Android 16 Developer Preview 1 Highlights Schedule and Compatibility
- Valuations for the IT industry Morgan Stanley is not cheap, but it is also not in the sell zone:
- Job Opportunity in IT sector to rise in 2025: Report
- Growing Cybersecurity Risks in the Digital Age .
- SBI cautions customers to save money!!
- SPADEX: a twin satellite mission
- QR codes are increasingly being scanned in India! UPI is the most prevalent transaction mechanism in rural and semi-urban India.
- The iPhone 17 Air is set to be released in 2025, with foldable Apple devices expected by 2026?
- The Advantages of Outsourcing Software Development :
- YouTube says it will to remove videos in India that have clickbait titles and thumbnails
- The Textile Industry Evolutionary Response to Artificial Intelligence::
- Review of Apple Watch Series 10 Value for Money and Time
- What is Education ERP and Why Do You Need It
- An increase in digital transformation deals in FY25 signals a return to growth according to IT businesses---
- Wipro will pay 40 million dollar to acquire Applied Value Technologies an IT consulting firm:
- Is tech industry already on cusp of artificial intelligence slowdown?
- Top Benefits of Using Education ERP
- LTIMindtree creates an AI-powered Cyber Defense Resiliency Center:
- IT Professionals Quit C-Suites for AI Ventures:
- Google efforts to regulate targeted advertising in the United Kingdom have sparked concern:
- Revolutionizing Academic Management Top Education ERP Examples:
- 2024 will be the year of AI-powered PC and Macs
- WhatsApp Web is finalising a feature that lets users search images from Google in reverse Here's how:
- Seeing cyber threats in 2024 Key events and what might be expected in 2025:
- Education ERP Software: An Overview
- Revolution in Indian AI & Data Centre A global force in the making:
- Technologies to watch in 2025 A Comprehensive Guide:
- Know how advanced features make education ERP systems requirements for any institution:
- Out of all the stock in cloud computing, which one will perform the best for the year ending at 2025?
- YouTube statistics 2025 demographics users by country and more:
- 40 plus web development sites that will change the way one build websites in 2025:
- Introduction to Education ERP Solutions:
- Tata Electronics looks way beyond Apple and wants to create for Xiaomi and Oppo:
- Top AI Search Engines for 2025:
- Operator an OpenAI agent that handles web tasks
- Step-by-Step Guide to Implement Education ERP
- DeepSeek AI: The Chinese AI App that has World talking
- Web Technology Trends in 2025: Generative AI
- Developing Enterprises Preparing For Upcoming Trends In 2025 Technology:
- Meta AI will get more personalised by using data from WhatsApp, Messenger and Facebook
- AI Tools Together With Their Techniques Which Will Be Prominent In 2025.
- IT Industry applauds Budget 2025's emphasis on skilling, Make in India and more.
- Overcoming Education ERP Deployment Hurdles
- DeepSeek R1: Multiple security flaws in iOS app, recent findings reveal
- Google made its most experienced AI models for public access, major achievement in its virtual agent project:
- Amazon has announced a hardware event to launch a new Alexa feature on 26th of Feb 2025:
- Google Messages to soon get WhatsApp video calling support
- Best Practices for a Successful Education ERP Rollout:
- Instagram announces teen accounts with parental control in India
- OpenAI denies to use the content of Indian media groups in training:
- Apple co-operates with SpaceX and T-mobile for Starlink satellite connectivity on Iphones:
- JioHotstar is launched as the merger of Jio, Hotstar by the Reliance:
- 7 Steps to Implement Education ERP
- Facebook updated its policy concering Live Videos and now they will be deleted 30 days afterwards.
- Government orders ban on 119 apps on Google Play Store on National security ground
- A UK study has revealed that AI Generated content increases the risk of bank runs.
- Karnataka tourism goes digital: Interactive new platform.
- Maharashtra Government working on a dedicated AI policy, developing GCC parks
- Instagram Reels may be set its stand-alone app: Report
- Adobe launch free Photoshop App in a bid for young users:
- Google is working to replace SMS-based two-factor authentication from Gmail with QR codes:
- Skype is gradually shutting down to drive its users towards Microsoft Teams:
- The True Cost of Implementing Education ERP
- Microsoft will be releasing its AI app, Dragon Copilot exclusively for the healthcare.
- Google is warning Chrome users to delete these 16 popular extensions immediately.
- Netflix email scam alert: Netflix members don't open emails with this subject line.
- Google trials an AI-exclusive version of its search engine.
- The newly introduced Gemini 2.0 Flash AI model for image generation comes with exciting possibilities.
- Amazon is putting more intelligence into Alexa.
- Comprehensive Guide to Education ERP Integration
- Hackers could hijack your life through one phone call: See how this merging calls scam work.
- NPCI is going to unlink UPI on such numbers starting from 1 April: Check and see if you are one of them.
- Swiggy instamart starts 10-minute phone delivery across 10 cities.
- Choosing the Best School ERP System.
- Importance of Technology:
- The best AI tools (Tested and Tried)
- Check point report warns: PDFs are the latest cyber weapon of choice.
- The best and trending AI tools: Tested by technology.
- Top School ERP Software:
- The increasing risk of a mule account: when fraudsters use your bank account.
- PhonePe launches “UPI circle” for shared payments:
- Top Features of School ERP Software:
- Google's new prompt engineering playbook: 10 key points on mastering Gemini, and other AI tools.
- AI-generated background music tool was launched by YouTube for creators.
- Affordable School ERP Solutions
- India ready to work magic of UPI with AI:
- Evolution of fraud detection: From static rules to AI insight analytics:
- Four steps to authorize people's with AI fluency:
- Benefits of School Management Software:
- ChatGPT Adds Shopping Help, Increasing Competition with Google:
- Top University ERP Solutions for 2025:
- Open AI is negotiating with Microsoft for fresh funds and future IPO, reports FT:
- Request a School ERP Software Demo Today.
- Google releases “AI Mode” in the next phase of its journey to change search
- I/O Edition: Google has announced everything at the Android show: Android 16.
- The Best ERP for Higher Education.
- Gemini smarts are arriving on more Android devices:
- Top ERP solutions for universities
- Google begins to show ads in AI Mode, extends AI Overview ads to desktop search:
- Finally, after 15 long years, WhatsApp arrives on iPad.
- Must-have features in university ERP software.
- TRAI is not calling: Frauders impersonating officials are fooling even the smartest.
- Benefits of ERP in higher education
- Google Gemini now supports scheduled actions, launches a new Live swipe gesture.
- How to make UPI payments offline.
- WhatsApp will soon utilize Meta AI to summarize unread messages: Here's how it works
- Meta AI and Edits app now allows you to edit videos with generative AI.
- Google is now testing the Search-Live feature with AI Mode.
- How India's e-commerce companies are quietly becoming smarter with AI tools from Microsoft.
- Samsung is likely to launch its very first Android XR headset in the near future and here is everything we know about it.
- Choosing the Right ERP for Universities
- SparkKitty, a new malware that steals screenshots from your phone: Everything you need to know
- Doppl, Google’s new app that allows users to try new clothes digitally
- Advantages of Cloud-Based Education ERP
- Google’s customizable Gemini chatbots are now in Docs, Drive, Sheets, and Gmail
- BitChat; Jack Dorsey's messaging app that works without internet using Bluetooth Know its features and how it works
- Key Benefits of Cloud ERP Systems
- Web Development Trends for 2025
- Cloud vs On-Premise Education ERP
- Top Cloud ERP Providers for Education
- Google’s Gemini 2.5 Deep Think, now available to Google AI Ultra subscribers
- Showrunner, the AI that can generate entire episodes of TV shows
- How Cloud ERP is Transforming Education
- Get Pricing for Cloud ERP Solutions Today
- IT & BPM Industry in India
- Why Choose a Customizable ERP for Education
- Apple, Google and Meta are working to perfect a science fiction gadget: The Universal Translator
- Tailored ERP Solutions for Education
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): its Importance, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Cryptocurrency
- Data is the New Gold of the Economy
- Digital Transformation in the Tourism Sector
- The Benefits of Modular Education ERP
- ERP Customization: Solutions for Schools
- The most common types of scams in India
- Personalized Education ERP Software
- Customizable Features in ERP Systems
- Ensuring Data Security with Education ERP
- How Secure ERP Systems Benefit Education
- OpenAI testing to launch impression-based ads in ChatGPT
- Stop Partitioning Your SSDs; Learn Why should you not partition SSDs
- Data Protection Best Practices in Education ERP